Sure, you want to do the right thing as an entrepreneur, small business owner, or IT manager in order to offer your clients privacy and security in your small to medium entreprise. But it seems such a complex mix of legal and technical issues. Where to start implementing data privacy?
The foundational principles were laid out in 2011 by Ann Cavoukian, Ph.D, a former three-term Information & Privacy Commissionner for the province of Ontario in Canada.
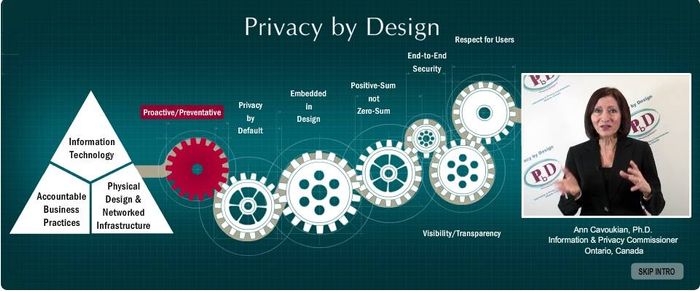
Outline of Privacy by Design by Ann Cavoukian:
Privacy by Design is a concept I developped back in the 90’s, to address the ever-growing and systemic effects of Information and Communication Technologies, and of large-scale networked data systems. Privacy by Design advances the view that the future of privacy cannot be assured solely by compliance with regulatory frameworks; rather, privacy assurance must ideally become an organization’s default mode of operation.
Initially, deploying Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) was seen as the solution. Today, we realize that a more substantial approach is required — extending the use of PETs to PETS Plus — taking a positive-sum (full functionality) approach, not zero-sum. That’s the “Plus” in PETS Plus: positive-sum, not the either/or of zero-sum (a false dichotomy).
Privacy by Design extends to a “Trilogy” of encompassing applications:
- IT systems
- accountable business practices
- physical design and networked infrastructure.
Principles of Privacy by Design may be applied to all types of personal information, but should be applied with special vigour to sensitive data such as medical information and financial data. The strength of privacy measures tends to be commensurate with the sensitivity of the data.
The objectives of Privacy by Design — ensuring privacy and gaining personal control over one’s information and, for organizations, gaining a sustainable competitive advantage — may be accomplished by practicing the following 7 Foundational Principles.
1. Proactive not Reactive; Preventative not Remedial
The Privacy by Design (PbD) approach is characterized by proactive rather than reactive measures. It anticipates and prevents privacy invasive events before they happen. PbDdoes not wait for privacy risks to materialize, nor does it offer remedies for resolving privacy infractions once they have occurred — it aims to preventthem from occurring. In short, Privacy by Design comes before-the-fact, not after.
2. Privacy as the Default Setting
We can all be certain of one thing — the default rules! Privacy by Design seeks to deliver the maximum degree of privacy by ensuring that personal data are automatically protected in any given IT system or business practice. If an individual does nothing, their privacy still remains intact. No action is required on the part of the individual to protect their privacy — it is built into the system, by default.
3. Privacy Embedded into Design
Privacy by Design is embedded into the design and architecture of IT systems and business practices. It is not bolted on as an add-on, after the fact. The result is that privacy becomes an essential component of the core functionality being delivered. Privacy is integral to the system, without diminishing functionality.
4. Full Functionality — Positive-Sum, not Zero-Sum
Privacy by Design seeks to accommodate all legitimate interests and objectives in a positive-sum “win-win” manner, not through a dated, zero-sum approach, where unnecessary trade-offs are made. Privacy by Design avoids the pretense of false dichotomies, such as privacy vs. security, demonstrating that it ispossible to have both.
5. End-to-End Security — Full Lifecycle Protection
Privacy by Design, having been embedded into the system prior to the first element of information being collected, extends securely throughout the entire lifecycle of the data involved — strong security measures are essential to privacy, from start to finish. This ensures that all data are securely retained, and then securely destroyed at the end of the process, in a timely fashion. Thus, Privacy by Design ensures cradle to grave, secure lifecycle management of information, end-to-end.
6. Visibility and Transparency — Keep it Open
Privacy by Design seeks to assure all stakeholders that whatever the business practice or technology involved, it is in fact, operating according to the stated promises and objectives, subject to independent verification. Its component parts and operations remain visible and transparent, to users and providers alike. Remember, trust but verify.
7. Respect for User Privacy — Keep it User-Centric
Above all, Privacy by Design requires architects and operators to keep the interests of the individual uppermost by offering such measures as strong privacy defaults, appropriate notice, and empowering user-friendly options. Keep it user-centric.
So now you know the theory upon which the broundbreaking European privacy law GDPR was based upon. Now what ?
Tech for Good Canada is holding an open online discussion January 20, 2021 on this titled: ‘Does Tech Mean Surveillance by Design ?’ Join us by registering, free of charge, to the (private-by-design) Livestorm meeting here.







